Understanding Node Types in n8n
At the heart of every n8n workflow are nodes—the fundamental units that perform tasks, control logic, and manage data flow.
To build effective workflows in n8n, it's essential to understand the different types of nodes and how each one plays a unique role. This article covers the five primary node categories in n8n:
- Trigger Nodes
- Action Nodes
- Utility Nodes
- Code Nodes
- AI Agent Node
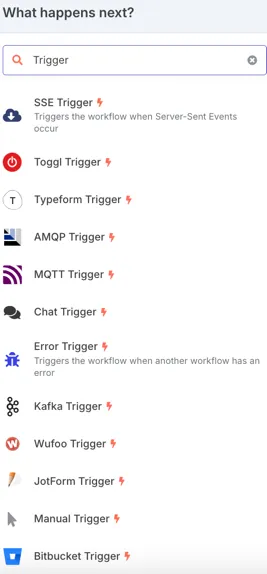
🟢 1. Trigger Nodes: The Starting Point of Every Workflow
Trigger Nodes initiate workflows. They monitor for specific events or conditions and automatically start the workflow when those conditions are met. Think of them as the "entry points" or "watchers" that detect when something interesting happens.
Common Use Cases:
- Receiving a new webhook from an external system
- Detecting a new message in Slack
- Scheduling tasks to run daily at 9 AM
- Monitoring for new email replies or form submissions
Popular Trigger Nodes:
- Webhook: Starts the workflow upon receiving an external HTTP request
- Schedule: Executes workflows based on time-based triggers (cron jobs)
- Email Trigger: Watches for incoming emails
- RSS Feed Trigger: Monitors for feed updates
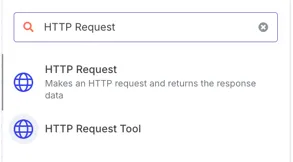
🟡 2. Action Nodes: Do Something With the Data
Once a workflow begins, Action Nodes perform tasks by interacting with external services. These nodes create records, send messages, or post data.
Common Use Cases:
- Sending messages in Microsoft Teams or Slack
- Creating or updating records in Airtable, Notion, or Google Sheets
- Sending transactional emails or SMS
- Uploading files to Google Drive or S3
Examples of Action Nodes:
- HTTP Request: Sends customizable HTTP calls to any API
- Airtable: Create, update, or find records
- Send Email: Dispatches emails via SMTP or third-party providers
- Discord: Posts messages to a channel or direct messages
🔧 3. Utility Nodes: The Data Transformers
Utility Nodes don't communicate with external apps. Instead, they transform, filter, or restructure data inside the workflow—essential for shaping data to meet downstream requirements.
Common Use Cases:
- Filtering data based on conditions
- Looping through arrays
- Converting data formats (e.g., JSON to CSV)
- Merging datasets
Key Utility Nodes:
- IF: Implements conditional logic (if/else)
- Set: Creates or modifies data fields
- SplitInBatches: Breaks up large datasets for sequential processing
- Merge: Combines multiple inputs into a single output
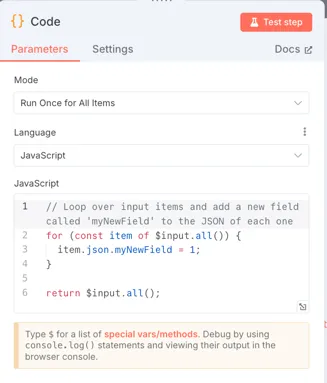
🧠 4. Code Nodes: Injecting Custom Logic
For developers and power users, Code Nodes offer the ability to write JavaScript directly inside the workflow. These nodes bridge visual programming with traditional scripting, giving you full control over logic.
When to Use:
- Custom data manipulation not handled by standard nodes
- Integrating APIs without official n8n support
- Adding fallbacks, validations, or transformations
Main Code Nodes:
- Function: Runs custom JavaScript using current workflow items
- FunctionItem: Executes JavaScript on each item individually
- HTTP Request: A multipurpose tool for direct API calls
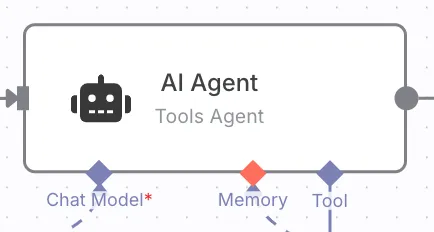
🤖 5. AI Agent Node: The Smart Brain of Your Workflow
The AI Agent Node introduces intelligent behavior into workflows. Powered by large language models (LLMs) like GPT, this node can interpret, summarize, classify, or generate content based on unstructured data such as emails or chats.
Practical Use Cases:
- Auto-tagging support tickets
- Summarizing emails or long reports
- Creating captions from product descriptions
- Making routing or reply decisions dynamically
Capabilities:
- Compatible with OpenAI, Azure, Hugging Face, or self-hosted LLMs
- Supports prompt chaining, memory, and multi-turn interactions
- Seamlessly integrates into workflows for natural language understanding
🧩 Putting It All Together
A complete n8n workflow might look like this:
- Trigger Node: Webhook receives a new user registration
- Utility Node: Set normalizes the user data
- Code Node: Function calculates a custom welcome message
- AI Agent Node: GPT generates a personalized onboarding email
- Action Node: The email is sent using SendGrid
Each node plays a distinct and critical role in translating business logic into functional automation.
🎯 Final Thoughts
Understanding the types of nodes in n8n is foundational for mastering workflow automation. Whether you're building a simple task or a complex data pipeline, blending Trigger, Action, Utility, Code, and AI Agent Nodes gives you powerful flexibility.
As n8n evolves, expect to see even more advanced node types, tighter integrations, and deeper AI capabilities that continue to push the boundaries of what automation can do.
Thanks for reading!
Enjoyed this article? Subscribe to the newsletter to get notified when new posts go live.